What Two Fields Makeup Electromagnetic Waves
What is electromagnetic radiation?
Electromagnetic radiation is a type of free energy that is all around united states of america and takes many forms, such as radio waves, microwaves, Ten-rays and gamma-rays. Sunlight is also a form of electromagnetic free energy, but visible calorie-free is just a small portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, which contains a wide range of wavelengths.
When was electromagnetism discovered?
People have known nearly electricity and magnetism since ancient times, but the concepts were not well understood until the 19th century, according to a history from physicist Gary Bedrosian of the Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute in Troy, New York. In 1873, Scottish physicist James Clerk Maxwell showed that the 2 phenomena were connected and developed a unified theory of electromagnetism, according to Live Science sister site Space.com. The study of electromagnetism deals with how electrically charged particles collaborate with each other and with magnetic fields.
Maxwell developed a prepare of formulas, called Maxwell'due south equations, to describe the different interactions of electricity and magnetism. Though at that place were initially twenty equations, Maxwell after simplified them to only four bones ones. In uncomplicated terms, these 4 equations land the post-obit:
- The force of attraction or repulsion between electric charges is inversely proportional to the foursquare of the distance between them.
- Magnetic poles come in pairs that concenter and repel each other, much as electric charges do.
- An electric current in a wire produces a magnetic field whose management depends on the management of the current.
- A moving electric field produces a magnetic field, and vice versa.
How is electromagnetism created?
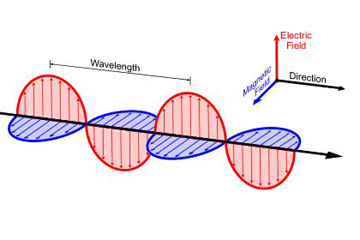
Electromagnetic radiations is created when a charged diminutive particle, such every bit an electron, is accelerated by an electric field, causing it to move. The movement produces aquiver electric and magnetic fields, which travel at right angles to each other, according to an online physics and astronomy form from PhysLink.com. The waves have certain characteristics, given every bit frequency, wavelength or free energy.
A wavelength is the distance betwixt two consecutive peaks of a wave, according to the Academy Corporation for Atmospheric Inquiry (UCAR). This distance is given in meters or fractions thereof. Frequency is the number of waves that grade in a given length of time. Information technology is usually measured as the number of wave cycles per 2d, or hertz (Hz). A brusk wavelength means that the frequency will be higher considering i cycle tin pass in a shorter amount of time. Similarly, a longer wavelength has a lower frequency because each cycle takes longer to consummate.
What are the parts of the electromagnetic spectrum?
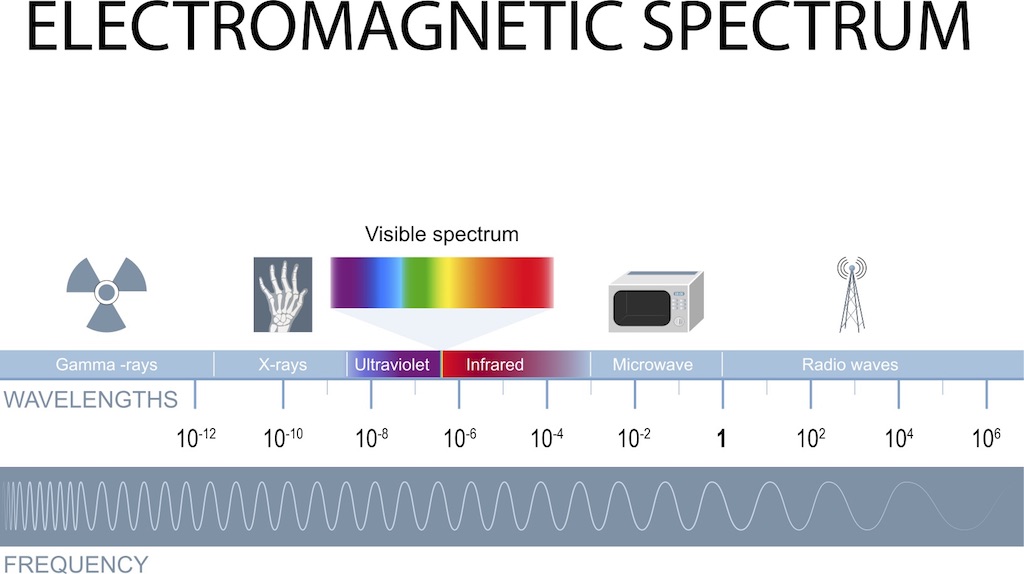
Electromagnetic radiation spans an enormous range of wavelengths and frequencies. This range is known as the electromagnetic spectrum, co-ordinate to UCAR. The electromagnetic spectrum is mostly divided into seven regions, in order of decreasing wavelength and increasing energy and frequency. The mutual designations are radio waves, microwaves, infrared (IR), visible calorie-free, ultraviolet (UV) light, X-rays and gamma-rays.
Radio waves
Radio waves are at the lowest range of the electromagnetic spectrum, with frequencies of upwardly to about 30 billion hertz, or 30 gigahertz (GHz), and wavelengths greater than virtually 0.4 inch (10 millimeters). Radio is used primarily for communications, including vocalism, data and entertainment media.
Microwaves

Microwaves fall in the range of the electromagnetic spectrum betwixt radio and IR. They take frequencies from about 3 GHz to 30 trillion hertz, or xxx terahertz (THz), and wavelengths of well-nigh 0.004 to 0.four inch (0.1 to 10 mm). Microwaves are used for loftier-bandwidth communications and radar, too as for a heat source for microwave ovens and industrial applications.
Infrared
Infrared is in the range of the electromagnetic spectrum between microwaves and visible lite. IR has frequencies from about 30 to 400 THz and wavelengths of about 0.00003 to 0.004 inch (740 nanometers to 100 micrometers). IR light is invisible to human eyes, merely we can experience it as oestrus if the intensity is sufficient.
Visible calorie-free
Visible light is found in the middle of the electromagnetic spectrum, betwixt IR and UV. It has frequencies of virtually 400 to 800 THz and wavelengths of most 0.000015 to 0.00003 inch (380 to 740 nanometers). More generally, visible light is defined equally the wavelengths that are visible to most human optics.
Ultraviolet
Ultraviolet low-cal is the range of the electromagnetic spectrum between visible light and X-rays. Information technology has frequencies of about 8 × 1014 to 3 x 1016 Hz and wavelengths of about 0.0000004 to 0.000015 inch (10 to 380 nanometers). UV light is a component of sunlight, but it is invisible to the homo middle. Information technology has numerous medical and industrial applications, simply information technology tin harm living tissue.
X-rays
Ten-rays are roughly classified into two types: soft 10-rays and hard Ten-rays. Soft X-rays make up the range of the electromagnetic spectrum between UV and gamma-rays. Soft Ten-rays accept frequencies of about iii × xsixteen to x18 Hz and wavelengths of nearly 4 × 10−7 to 4 × ten−8inch (100 picometers to 10 nanometers). Difficult Ten-rays occupy the same region of the electromagnetic spectrum as gamma-rays. The only divergence between them is their source: X-rays are produced by accelerating electrons, while gamma-rays are produced by diminutive nuclei.
Gamma-rays
Gamma-rays are in the range of the spectrum in a higher place soft X-rays. Gamma-rays have frequencies greater than virtually 1018 Hz and wavelengths of less than 4 × x−9inch (100 picometers). Gamma radiation causes damage to living tissue, which makes information technology useful for killing cancer cells when practical in advisedly measured doses to small regions. Uncontrolled exposure, though, is extremely dangerous to humans.
This commodity was updated on March 17, 2022, by Live Science contributor Adam Mann.
Additional resources
- Explore the electromagnetic spectrum further with this interactive page from NASA.
- Convert between wavelength and frequency and acquire the size of different electromagnetic waves with this reckoner from HyperPhysics, a website hosted by Georgia Country University.
- Read James Clerk Maxwell'due south groundbreaking 1873 treatise on electricity and magnetism online.
Bibliography
Sutter, P. (2021, September 29). Who was James Clerk Maxwell? The greatest physicist yous've probably never heard of. Space.com. https://world wide web.space.com/who-was-james-clerk-maxwell-physicist
University Corporation for Atmospheric Research, Center for Scientific discipline Education. (2017). Electromagnetic (EM) spectrum. https://scied.ucar.edu/learning-zone/atmosphere/electromagnetic-spectrum
University Corporation for Atmospheric Research, Center for Science Education. (2018). Wavelength. https://scied.ucar.edu/learning-zone/atmosphere/wavelength
Walorski, P. (n.d.). Why is that electrons radiate electromagnetic energy when they are accelerated? PhysLink.com. Retrieved March 17, 2022, from https://www.physlink.com/education/askexperts/ae436.cfm
What Two Fields Makeup Electromagnetic Waves,
Source: https://www.livescience.com/38169-electromagnetism.html
Posted by: bennerjusible.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Two Fields Makeup Electromagnetic Waves"
Post a Comment